
Many people from our organization and external companies cooperating with us are involved in handling deliveries: suppliers, consignees, carriers, forwarders, drivers, and logistics operators. Each participant in this logistics chain creates, transmits, and analyzes the information necessary for the efficient collection of packaging, materials, and raw materials as well as the delivery of finished products. A single process spread over many people, consists of a few or a dozen or so minutes’ worth of activities, requires efficient and error-free communication and quick access to up-to-date information.
A team of consultants and implementation specialists from LOGINTEGRA
and external consultants has developed an analysis of the labor consumption of handling a single delivery. The collected data was averaged thus allowing for an estimated comparison of the two methods of handling a given delivery broken down into individual activities.
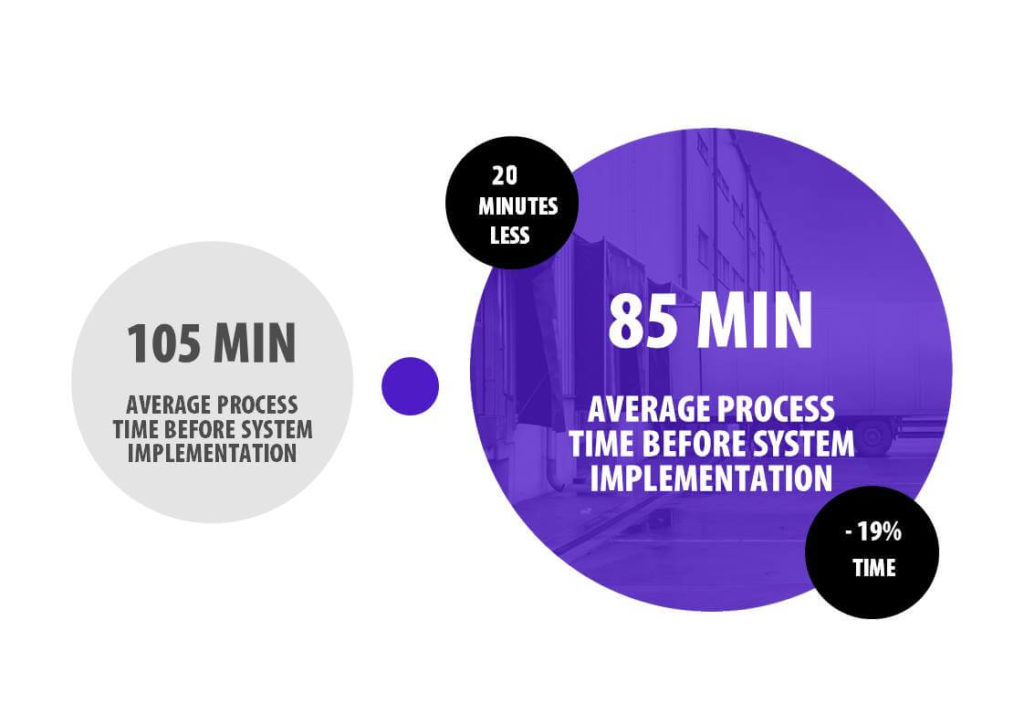
The comparison of traditional forms of communication of the participants in the supply chain (e-mail, telephone, messenger, etc.) with the use of the TIME SLOTS system shows that the average savings in terms of labor consumption can reach up to 19%. The analysis of the obtained results confirms that companies handling as few as approx. 10 deliveries and 10 shipments a day, if provided with the STANDARD package of the LOGINTEGRA system, can count on a return on investment after just 6 months. The savings resulting from a shortened process bring, after just two years, in addition to improved communication and planning in the online schedule, benefits amounting to tens of thousands of EUR a year. Of course, a greater number of unloading and loading operations per day scales up the presented results correspondingly, thus reducing the costs of handling deliveries and activating the additional potential of a warehouse, the departments involved in the process, or carrier companies.
Anyone interested in contacting LOGINTEGRA can count on an estimate of the level of savings and return on investment based on their own data on the number of unloading or loading operations.
